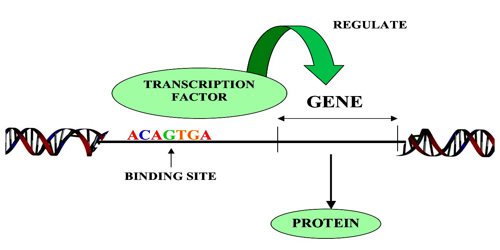
Transcription factors are proteins that control the transfer of information from the DNA sequence to mRNA by binding to a specific DNA sequence. These proteins interact with the accelerator group by binding to the enhancer and accelerator regions. These proteins, which are grouped according to their structural similarities, are DNA-specific proteins because they bind to different DNA sequences according to the differences in their structures [1]. This website has covered the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix DNA-binding transcription factors.
References
[1]: D. S. Latchman, "Transcription factors: an overview," The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, vol. 29, no. 12, pp. 1305-1312, 1997.