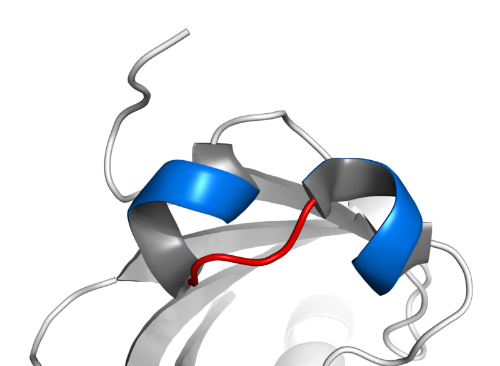
Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor proteins are a transcription factor protein found in almost all eukaryotes from plants to bacteria and humans, and play important roles in the regulation of conditions such as neurogenesis, myogenesis and cardiac development in animals [1].
It contains two alpha helical structures separated by a loop and a DNA binding site of 60 amino acids (basic) [1]. The word "foundation" refers to the chemistry of the motif, not the complexity of the structure. Usually, one helix is smaller and, due to the flexibility of the loop, it is folded over and packaged onto another helix, allowing dimerization. The larger helix contains DNA binding sites. bHLH transcription factor proteins E-box bind to a consensus sequence called CANNTG. The canonical E-box is CACGTG (palindromic), but some bHLH transcription factors, particularly those in the bHLH-PAS family, bind to related non-palindromic sequences similar to the E-box. bHLH TFs can homodimerize or heterodimerize with other bHLH TFs and form a wide variety of dimers, each with specific functions [2]. The helical structures allow interaction with other bHLH proteins. Nineteen amino acids in the domain are highly conserved in almost all living things, from yeast to humans. It has important roles in the development, cell proliferation and differentiation of vertebrates. However, not much information is known about their evolution and differentiation [1], [3].
"These clades are classified into five major groups based on their basic DNA-binding patterns (Atchley and Fitch 1997; Ledent and Vervoort 2001). Group A proteins bind to the hexanucleotide CAGCTG E-box and include proteins such as Lyl, Twist, dHand, Achaete-Scute, Atonal, MyoD, and E12. Group B proteins bind to the CACGTG E-box, also known as G-box in plants, and include Srebp, Tfe, Myc, Mad, Mxil, Cbf1, ESC, R, and G-box. Group C proteins, including Sim, Trh, and Ahr, have an uncharacteristic basic region and contain a pair of PAS repeats, which facilitates dimerization with other PAScontaining proteins. Group D proteins lack the basic DNA binding region and act as dominant negative regulators of other bHLH proteins and include Id and Emc. Recently an additional group E has been described that includes Gridlock, E(spl), Hey, and Hairy (Ledent and Vervoort 2001). This latter group contains proline or glycine residues within the basic region and shows a preference to bind the sequence CACGNG (Steidl et al. 2000; reviewed by Fisher and Caudy 1998)." [4].
Table 1. Helix-loop-helix transcription factors: Protein families, functions, and motifs [5]
|
Protein families |
Included proteins |
Groupings |
Function |
||
|
E- box |
Murre et al. |
LZ |
|||
|
AC-S |
ac, sc, ase, l’sc, mash, ash |
A |
II |
|
Neurogenesis; determination of neuronal precursors |
|
ATONAL |
atonal, lin-32, math1, neuroD |
A |
|
|
Neurogenesis |
|
DELILAH |
delilah |
A |
|
|
Differentiation of epidermal cells into muscle |
|
dHAND |
dhand, ehand, hxt, hed |
A |
|
|
Rardiac morphogenesis; trophoblast cell development |
|
E12/Da |
e12, e47, itf, pan, G12, me2, da |
A |
I |
|
Neurogenesis, sex determination; regulation of myogenesis |
|
HEN |
hen, helhel |
A |
|
|
Neurogenesis |
|
LYL |
lyl, scl, nscl, tal |
A |
|
|
Hematopoietic proliferation and differentiation |
|
MYOD |
myod1, myogenin, myf5, myf6 |
A |
II |
|
Myogenesis |
|
NEX |
nex-1, rat4 |
A |
|
|
Neurogenesis |
|
TWIST |
twist, ec2, paraxis, scleraxis, dermo |
A |
|
|
Specification of mesoderm lineages |
|
ARNT |
arnt |
B |
|
|
Regulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor activity |
|
CBF |
cbf-1 |
B |
|
|
Rentromeric binding and chromosomal segregation |
|
ESC |
esc1 |
B |
|
|
Sexual differentiation in yeast |
|
G-Box |
G-box |
B |
|
|
|
|
HAIRY |
hlhm, hairy, hes, deadpan, e(spl) |
B |
VI |
|
Neurogenesis; segmentation |
|
MAD |
mad, mxi1 |
B |
IV |
Yes |
Regulation of cell proliferation |
|
MYC |
c-myc, n-myc, l-myc, max |
B |
III |
Yes |
Cell proliferation, differentiation; oncogenesis |
|
NO |
ino2, ino4 |
B |
|
|
Phospholipid synthesis |
|
PHO4 |
pho4, nuc1 |
B |
|
|
Phosphate regulation in yeast |
|
R |
r, delila |
B |
|
|
Regulation of anthcynanin pigmentation |
|
SREBP |
srebp, add1, hlh106 |
B |
|
Yes |
Sterol synthesis; adipocyte determination |
|
TFE |
tfe3, tfeb, mi |
B |
III |
Yes |
Activates transcription in immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer |
|
USF |
usf, spf1, namalwa |
B |
|
Yes |
Upstream stimulation factor; insulin enhancer |
|
SIM |
sim, trh, ah |
C |
|
|
Central nervous system midline lineage regulation; tracheal cell induction |
|
ID |
id, heira, emc, hlh462 |
D |
V |
|
Negative inhibition of DNA binding; myogenesis, neurogenesis |
|
CENPBR |
cenpbr |
? |
|
|
Centromeric binding protein |
|
AP-4 |
ap-4 |
? |
|
Yes (2) |
Enhance viral and cellular gene activation |
References
[1]: S. Jones, "An overview of the basic helix-loop-helix proteins," Genome Biology, vol. 5, no. 6, p. 226-226, 2004.
[2]: https://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00010
[3]: V. Ledent and M. Vervoort, "The basic helix-loop-helix protein family: comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis," Genome Res., vol. 11, no. 5, p. 754-770, 2001.
[4]: M. J. Buck and W. R. Atchley, "Phylogenetic Analysis of Plant Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins," Journal of Molecular Evolution, vol. 56, no. 6, p. 742-750, 2003.
[5]: W. R. Atchley and W. M. Fitch, "A natural classification of the basic helix-loop-helix class of transcription factors," Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 94, no. 10, p. 5172-5176, 1997.